Why are we an Impact Tech?
Number of Slots Available Through FIES
The program peaked in 2014
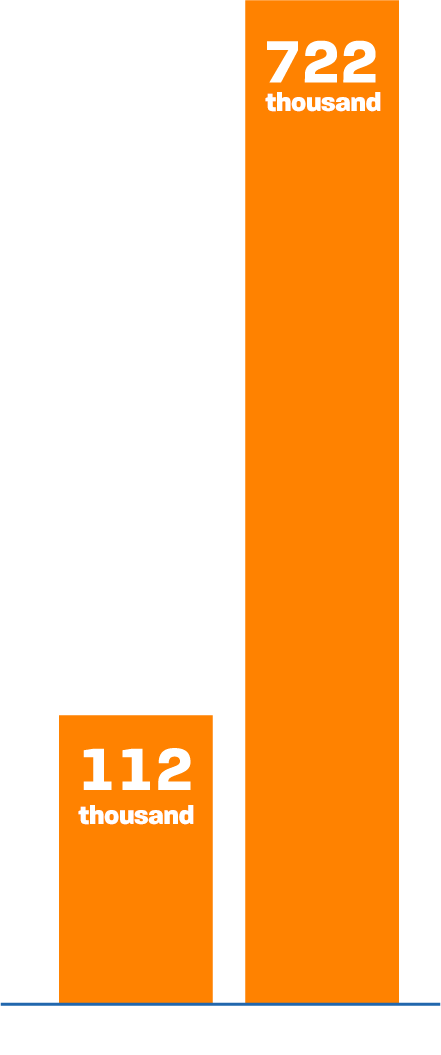
Education in Brazil faces numerous challenges, including a lack of resources, unequal access, and poor quality.
According to INEP, more than 50% of high school students do not complete their studies, and many who do struggle to find jobs due to a lack of practical skills and experience.
Without proper investment, millions of young Brazilians are deprived of essential educational opportunities. Education is a fundamental human right and a powerful tool to reduce poverty and social inequalities. We need initiatives that promote equitable access to quality education for all.
Number of Slots Available Through FIES
The program peaked in 2014
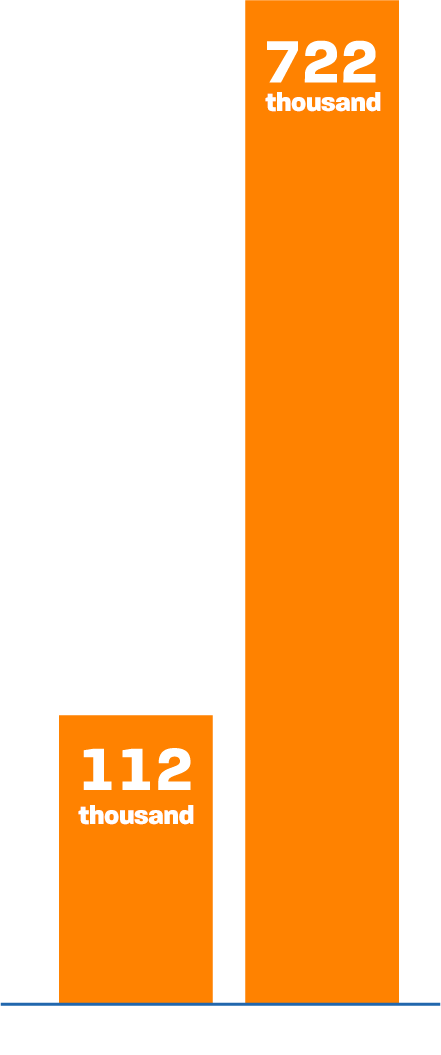
Education in Brazil faces numerous challenges, including a lack of resources, unequal access, and poor quality.
According to INEP, more than 50% of high school students do not complete their studies, and many who do struggle to find jobs due to a lack of practical skills and experience.
Without proper investment, millions of young Brazilians are deprived of essential educational opportunities. Education is a fundamental human right and a powerful tool to reduce poverty and social inequalities. We need initiatives that promote equitable access to quality education for all.
Panorama of College Education in Brazil
College education in Brazil faces a series of challenges that directly impact students’ education and future prospects. Among the main problems are school dropout, unemployment and lack of opportunities. Below is a detailed overview of these issues.
Dropping out of school is one of the biggest challenges facing higher education in Brazil. According to data from the National Institute of Studies and Educational Research Anísio Teixeira (INEP), the dropout rate in Brazilian higher education is around 30% in the first years of the course. The main factors that contribute to this dropout include:
- Financial Difficulties: Many students face difficulties in paying for tuition and other expenses related to education, leading them to drop out of school.
Work and Study: The need to work to support the family often prevents students from dedicating themselves fully to their studies, resulting in dropout.
Lack of motivation: The lack of connection between academic content and the job market can demotivate students, leading to dropout.
Unemployment among graduates is a significant issue in Brazil. Although higher education is seen as a pathway to better job opportunities, many graduates struggle to enter the job market. Data from the Brazilian Institute of Geography and Statistics (IBGE) indicates that the unemployment rate among young people with a higher education degree is approximately 15.5%, higher than the national average.
Regional inequality also worsens the challenges of higher education in Brazil. Regions such as the North and Northeast face greater difficulties in terms of educational infrastructure, teaching quality, and access to resources.
- Deficient Infrastructure: Many higher education institutions in disadvantaged areas lack adequate infrastructure, compromising the quality of education.
- Lower Quality of Education: The quality of higher education varies significantly across regions, with institutions in urban areas generally achieving better results.
- Mismatch Between Curriculum and Market Needs: Often, higher education curricula are not aligned with market demands, resulting in training that does not adequately prepare students for available professions.
- Increased Competition: With the growing number of graduates, competition for job openings has intensified, making it harder for new graduates to enter the workforce.
The lack of opportunities for graduates is a critical issue directly related to dropout rates and unemployment. Students, especially those from lower-income backgrounds, often face barriers to accessing internships and jobs that could complement their academic education.
- Access to Internships: The lack of internship programs and integration between educational institutions and companies limits opportunities for students to gain practical experience.
- Networking: Many students do not have access to professional networks that could facilitate their entry into the job market, which is crucial in a competitive environment.
Regional inequality also worsens the challenges of higher education in Brazil. Regions such as the North and Northeast face greater difficulties in terms of educational infrastructure, teaching quality, and access to resources.
- Deficient Infrastructure: Many higher education institutions in disadvantaged areas lack adequate infrastructure, compromising the quality of education.
- Lower Quality of Education: The quality of higher education varies significantly across regions, with institutions in urban areas generally achieving better results.
Conclusion
College education in Brazil faces significant challenges that affect students’ education and employment prospects. School dropout, unemployment and lack of opportunities are interconnected issues that require attention and coordinated action from public policies, educational institutions and companies. Investments in infrastructure, internship programs and partnerships between the private sector and universities are essential to improve the current situation and promote more inclusive and quality higher education.
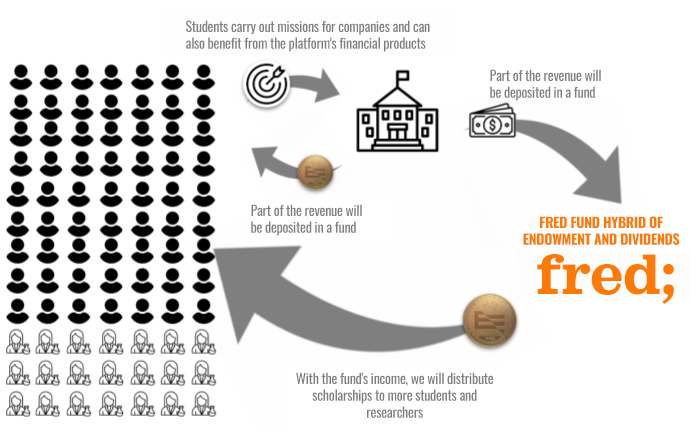
The mechanics of the fred fund;
Part of our startup’s revenue is allocated to a fund that distributes scholarships and scientific research grants. This fund is a way of reinvesting in the educational community, ensuring that each individual success contributes to collective success.
Multiplying the impact to generate a prosperous future:
The more engaged the student community is in FRED, the more students there will be in the future. Businesses are the engine of this transformation, funding missions that generate social impact. Together, we are creating a cycle of continuous growth and development.
We will create the community that will solve the education and research deficit in Brazil